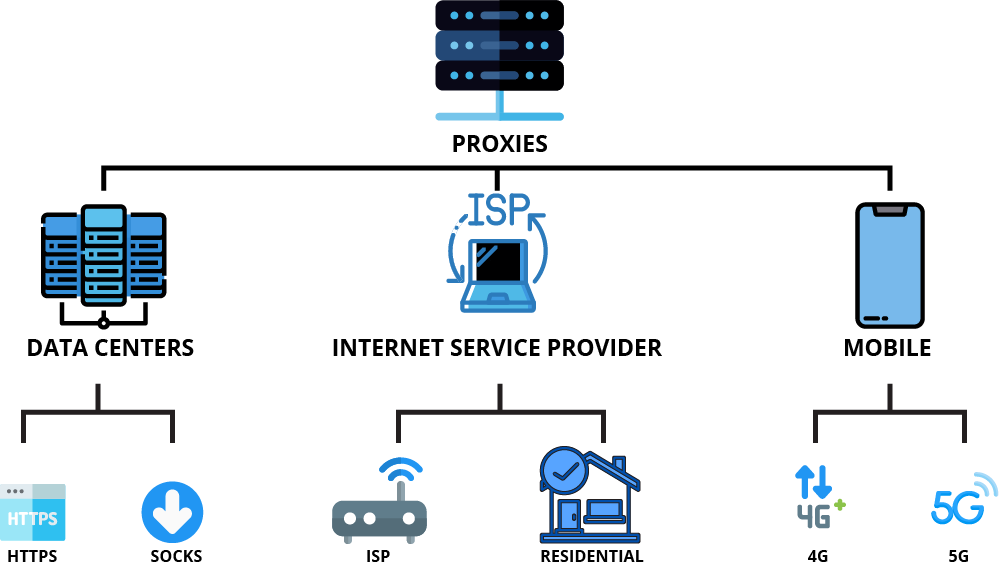
Proxy types: Definition, Comparison, and Guide
Proxy servers are commonly known as “proxies”. They are useful when there is a need for a new IP address. The reason for use varies. It can help access websites or contents that are unavailable in some countries. Some use it to protect the original IP address from automation and botting tasks. But how to determine the correct proxy types for your targets? Understanding their differences is the first step.
Proxy types based on:
Others:
Proxy type based on IP source
Data center Proxies
These proxies are generated from independent servers. They are created with no affiliation with third parties. Thus, making the proxy acquisition easy and hassle-free.
Residential proxies
Mobile proxies
These proxies are connected to the user’s data network. They are more expensive than residential proxies and are best for accessing mobile-only content.
Proxy type based on Protocol
HTTP Proxies
These proxies use the combination of HTTP and SSL protocols. It is easy to set up but it can only read HTTP or HTTPS traffic.
SOCKS Proxies
These proxies are not bound to any traffic, but it requires a technical setup and configuration. It does not read proxied traffic and is best for torrenting.
Proxy type based on Access
Private proxies
Offers exclusive access to one user. All its features are dedicated to the user’s target such as unshared bandwidth and speed.
Shared proxies
Accessed by two or more people simultaneously. The number of users who share the proxy depends on the provider.
Public proxies
Also known as free proxies. Since it’s open to the public, there are no restrictions on how many people can use the proxy at a given time.
Proxy type based on Request Transmission
Outbound proxies
Also known as forward proxies. These proxies receive requests from the client and forward it to the target domain. It’s used to access geo-restricted content, anonymous browsing, social media automation, sneaker botting, and more.
Inbound proxies
Proxy type based on IP type
Static proxies
These IP addresses do not change. Users can use the IP over multiple requests.
Dynamic proxies
It refers to IP addresses that change every request or at a given time frame.
Proxy type based on IP format
IPV4 proxies
The most common type of IP. It is widely used and has a short and simple format. Example :
111.222.33.44
IPV6 proxies
It is created to solve the shortage of IPV4s. It has a longer format to accommodate the growing demand for IP addresses. Example:
888A:1111:222:3333:4444:5555:6:77
What is the best proxy type for you?
Consider the following when choosing a proxy:
Goals
What are your activities (e.g., account creation, crawling, botting)?
Target site
Does it support ipv4 or ipv6?
Feature
Do you need unlimited bandwidth? Do you need privacy?
Cost
Is it cost-effective and practical?
Each type has unique functionality and different features. Pay close attention to which proxy type will serve your purpose, has the best value for your money, and will help achieve your goals efficiently.
What are NewIPNow proxies?
Datacenter
Private
IPV4
Static
HTTP/HTTPS
How to buy private proxies:
Get High-Performance Private Proxies @ $0.88/IP + $0.00/GB!